[JS] async / await 개념정리
이고잉님 강의를 듣고 정리했다.
await & async
promise가 콜백지옥을 무찌를 수 있는 좋은 방법이지만
그래도 코드가 복잡하기는 하다.
그래서 ES8 문법으로 await 과 async 가 추가되었다.
await 과 async 는 promise를 더 깔끔하게 사용할 수 있는 방법이다.
하지만 경우에 따라 더 좋은 방법들이 다르기때문에, 적절히 섞어서 활용하는 것이 필요하다.
promise 복습을 먼저 해보자
1초 후 텍스트 출력, 다시 2초후 텍스트 출력, 다시 3초후 텍스트를 출력하는 함수가 있다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
function timer(time) {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
setTimeout(() => {
resolve(time);
}, time);
});
}
console.log("start"); // 작업의 시작을 알리는 텍스트 출력
timer(1000)
.then((result) => {
console.log(result);
return timer(result + 1000);
})
.then((result) => {
console.log(result);
return timer(result + 1000);
})
.then((result) => {
console.log(result); // promise chain으로 작업을 연결
console.log("end"); // 작업의 끝을 알리는 텍스트 출력 코드를 비동기처리
});
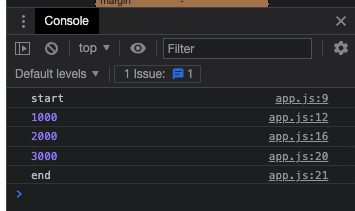
promise를 이용해서 콜백지옥을 탈출했다.
promise chain을 통해 여러 작업들을 병렬로 잘 정리했지만,
아직도 이 코드가 복잡해보였던 슨생님들은 더 좋은 것을 만들어내셨다.
await, async를 사용해 다시 정리해보자
await는 promise를 실행하는 코드를 마치 동기적으로 작동하는 코드처럼
깔끔하게 순서대로 적을 수 있게 하는 syntactic sugar 이다.
기본적으로는 promise 함수를 사용할때, 앞에 await를 붙이면 된다.
1
await timer(1000);
이렇게 실행하는 함수는 결국 promise에서 resolve에 정의되어있는 리턴값을 받아 오는데,
그값을 변수에 저장해서 다음 작업에 사용하면 된다.
1
2
let result = await timer(1000);
console.log(result);
하지만 이렇게 바꿔 실행하면
‘await는 async 함수 안에서만 실행할 수 있다’는 에러 문구가 뜬다.
그래서 await를 사용하려면 이렇게 바꿔줘야한다.
1
2
3
4
5
async function run() {
let result = await timer(1000);
console.log(result);
}
run();
async 가 앞에 붙은 함수를 만들어서 코드를 안에 넣고, 실행시켰다.
그래서 위에 then으로 병렬 정리했던 코드를 다시 한번 await를 사용해 바꿔 볼 수 있다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
async function run() {
console.log("start");
let result = await timer(1000);
console.log(result);
result = await timer(result + 1000);
console.log(result);
result = await timer(result + 1000);
console.log(result);
console.log("end");
}
run();
 위 then 메소드를 활용한 것과 동일한 결과를 얻을 수 있다.
위 then 메소드를 활용한 것과 동일한 결과를 얻을 수 있다.
비동기처리가 한번 더 필요하다면?
async 함수를 실행했는데, 또 앞 뒤로 시작과 끝을 알리는 메세지가 출력되게 하려면?
1
2
3
console.log("parent start");
run();
console.log("parent end");
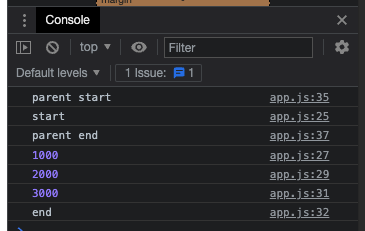
console.log('parent end') 는 동기적으로 실행되기 때문에 비동기코드(setTimeout)가 실행되기 전에 먼저 실행된 것을 볼 수 있다.
그렇다면 이 코드들이 비동기처리 될 수 있도록 다시한번 await 시켜줄 수 있다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
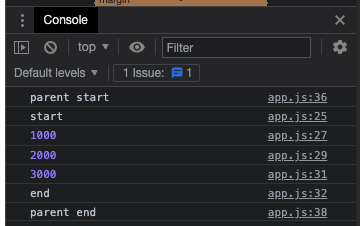
async function run2() {
console.log("parent start");
await run();
console.log("parent end");
}
run2();
💡
여기서 run 함수에 await 처리가 가능한 이유를 짚고가야한다.
console.log(run())으로 run 함수를 출력해보면
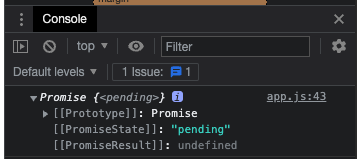
이렇게 promise 함수가 나오는 것을 확인해볼 수 있다.
async 함수는 또 다시 promise 함수를 리턴하는 것이다.
이것이 run()에도 다시 awiat를 붙이고, 그것을 다시 async 함수에 넣는 작업이 가능한 이유이다.

Leave a comment